Product Design
If you are going to create a brand new Product or renew an old one, the Care Studio Team can support you. The goal of Product Design is to solve user problems, fill market gaps, and achieve business objectives through a well-designed software product.
If you are going to create a brand new Product or renew an old one, the Care Studio Team can support you. The goal of Product Design is to solve user problems, fill market gaps, and achieve business objectives through a well-designed software product.
Product design is a multidisciplinary field focused on creating digital products that are both functional and user-friendly. It involves several key aspects:
User Experience (UX) Design: Ensuring the product is intuitive and meets the needs of its users.
User Interface (UI) Design: Crafting the visual elements of the product, such as layouts, colors, and typography.
Research and Strategy: Conducting user research, market analysis, and defining the product’s vision and goals.
Prototyping and Testing: Creating prototypes to test ideas and gather feedback before final development.
Collaboration: Working closely with engineers, product managers, and other stakeholders to bring the product to life
The Care Studio Team has so far supported the Product teams in the Prototyping and renewal of Unit overview, Unit overview for wards, Doctors orders and Precision medicine.
The Care Studio Team has so far supported the Product teams in the Prototyping and renewal of Unit overview, Unit overview for wards, Doctors orders and Precision medicine.
Innovation Projects
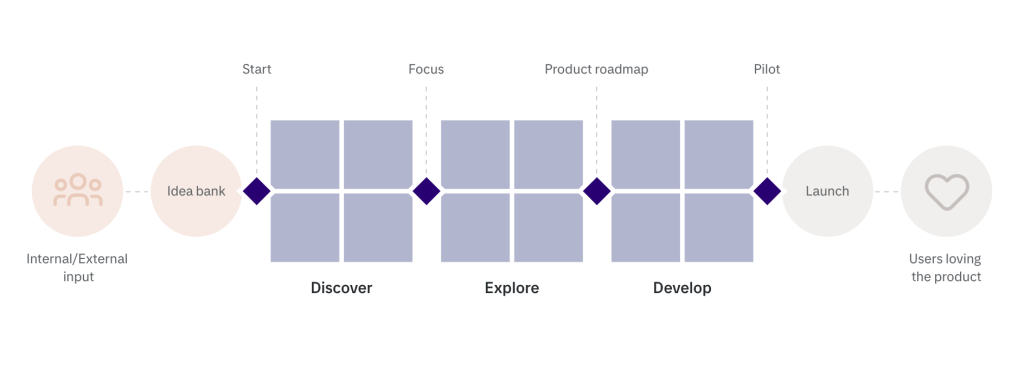
We structure innovation by using our holistic consumer/customer focused innovation process, where we take ideas and look at their potential by combining the user-, business- and technology perspectives.
Idea: Raw ideas are collected both from Tietoevry Care and from customers. Prioritize promising ideas based on their alignment with strategic goals and market demand. Generate a creative brief to adress goals for a Discover phase.
Discover: Conduct research to validate the feasibility and market potential. Gather data and insights through interviews, observations, surveys, and market analysis. Analyze user needs, market trends, and competitive landscape to identify opportunities.
Explore: Define metrics that are important to follow up on. Collaborate across teams to explore different approaches. Develop prototypes to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate the most promising concepts together with users and other important stakeholders.
Develop: Translate the ideas into actionable plans and detailed project specifications. Allocate resources and establish timelines for implementation. Collaborate between teams to develop prototypes, conduct testing, and refine solutions.
Launch: Execute the final product or service launch based on the developed plans. Implement marketing and communication strategies to create awareness and generate interest. Validate metrics and gather user feedback for a fact-based communication and to iterate and improve the offering over time.
Value Stoytelling
The storytelling is a “visionary” perspective describing the overarching aim of a Product(s), but also includes a clear value statements on what offering is today, and what it will be in the future.
Care Studio has a structured process to create relevant value stories that aligns with our Care Strategy and positioning. It assures alignment and push in our messaging and is an efficient way to create tangible results on Value Storytelling and adherent visualization.
In 2024 the Care Studio team has created Value Stories, together with the Product teams, for our three Product Launches: Lifecare Open Platform, Resource optimization and Data&AI.
Design Thinking
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements of business success.
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that prioritizes the user’s needs above all else, focusing on observing and understanding how people interact with their environments with empathy. It involves an iterative, hands-on approach to creating innovative solutions by continuously refining products or services based on real consumer engagement. Design thinking is human-centered, emphasizing evidence of how people actually engage with a product or service rather than assumptions. This approach aims to tackle complex problems by uncovering users’ pain points and providing solutions once identified, fostering innovation, creativity, and a more human-centered approach to problem-solving.
The key principles of design thinking include:
Human-centricity and empathy: Design thinking revolves around understanding human needs and user feedback, emphasizing empathy towards users to address their challenges and desires on a human level.
Collaboration: Design thinking encourages diverse, multidisciplinary teams to work together, fostering innovation and ensuring actionable guidance for the design process.
Generating ideas and solutions: Design thinking involves challenging assumptions, looking at problems from different perspectives, and developing multiple innovative solutions to address challenges effectively.
Redesign: All design is essentially redesign, focusing on fulfilling basic human needs or reaching desired outcomes through innovative solutions.
Tangibility: Making ideas tangible through prototypes helps communicate and test solutions effectively, enabling designers to iterate and refine their ideas based on real-world feedback.
Strategic Design
Strategic design uses design principles and methodologies to tackle complex challenges and drive innovation within organizations. It goes beyond traditional design boundaries, focusing not just on user experience and aesthetics but on how design decisions impact an organization’s strategic goals and capacity for innovation.
Connecting Strategic Goals: Strategic design ensures that design decisions align with an organization’s business goals. It sets metrics to measure these goals and connects projects with broader strategic objectives.
Analyzing Market Insights: It involves analyzing market trends, customer behavior, and the competitive landscape to identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
Keeping Up with Technological Trends: Strategic design keeps pace with emerging technologies, envisioning how they can improve products, services, and processes.
Considering Socio-economic Factors: It takes into account the social and economic context that shapes consumer needs and expectations, as well as the regulatory environment.
Understanding Environmental and Political Landscapes: Strategic design considers broader environmental issues, sustainability concerns, and political factors that can affect an organization’s strategy.
Creating Consistent Solutions: Strategic design ensures a seamless experience for end-users across different care levels and types, crucial for organizations with complex systems.
Fostering Innovation: It promotes a culture of innovation and adaptability, encouraging the development of new services, technologies, and approaches to meet evolving needs.
Promoting Collaboration: Strategic design encourages collaboration across various disciplines, leading to holistic solutions that consider the complex interplay of factors affecting health and well-being.
Accessibility
We assist others in understanding and implementing accessibility. We provide support in terms of explaining the concept of accessibility, conducting workshops, and guiding individuals on how to test accessibility using appropriate tools. We also review designs, considering factors such as touch target size, colors, and overall usability for users with diverse abilities.
Our team works to improve accessibility and ensure that it is integrated into all the projects we undertake through the following measures:
Testing and Compliance: We thoroughly test and ensure that our design system meets accessibility requirements. We strive to create inclusive experiences for all users by adhering to accessibility guidelines and standards.
Importance of Accessibility: We emphasize the importance of accessibility aspects in our projects using personas, thinking about inclusiveness and taking diversity into account. By considering diverse user needs and perspectives, we aim to create products that are accessible and inclusive for all.
Staying Up-to-Date: We stay updated with legislation such as the European accessibility act (EN 301 549), as well as accessibility guidelines such as WCAG 2.1/2.2. By staying informed, we ensure that our work aligns with current accessibility standards and requirements.
Spreading Awareness: We actively participate in communities and engage in initiatives like Keep Learning Week to spread awareness about accessibility. Through workshops and discussions, we help others understand what accessibility means for web applications and why it is important.
Ultimately, our goal is to integrate accessibility into our design DNA. We strive for accessibility to be a fundamental aspect of our design process and ensure that everyone can access and benefit from the digital products we create.
Business Development
Business development is like planting seeds for a flourishing garden. It’s about nurturing relationships, exploring new horizons, and creating opportunities that blossom into sustainable growth.
In essence, business development aims to drive long-term value and enhance an organization’s position in the market, and the Care Studio-team can you support you along this journey.
Business development refers to the strategic process of identifying and creating opportunities for sustainable growth within an organization. It involves activities such as:
Market Research: Analyzing market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscapes.
Lead Generation: Finding potential clients and building relationships.
Partnerships and Alliances: Collaborating with other businesses to expand reach.
Sales Strategies: Developing effective sales approaches.
Innovation: Creating new products, services, or business models.
Customer Workshops
Ideation workshops enhance customer relations and unlock new business opportunities.
Customer ideation workshops can be used to generate new ideas, refine current services, overcome obstacles and discover new opportunities. By bringing together different perspectives and experiences, new insights and ideas can be generated. It is also a great opportunity for you to gain a better understanding of your customers’ challenges and help find solutions in a creative and collaborative environment.
Planning and facilitation: We help plan and facilitate the workshop so that you can be a participant along with the customers.
Creative problem-solving tools and techniques: We adapt the workshop to the needs and wishes from you and your customers. Thanks to our experience and broad toolbox, we can tailor the day with creative problem-solving tools and techniques to inspire innovation and encourage out-of-the-box thinking.
Support and follow-up after the workshop: After the workshop, we compile the material that has been generated and create a summary that you can share with your customers. We are also here for continued support and guidance to work further on ideas generated during the session. Whether it’s doing further research, prototyping new concepts or testing with real customers.
Design System
Design systems play a pivotal role in care organizations, given the unique challenges and high stakes involved in this sector. Care systems, applications, and products need to be accessible, understandable, and usable by a diverse range of users, including patients, care professionals, and administrative staff. Here’s a closer look at why design systems are particularly significant in healthcare and social care.
User Experience: Care applications handle complex data and sensitive information. A design system simplifies these interfaces, reducing errors and enhancing patient care by making information easier to understand and actions easier to take.
Consistency: Consistency across platforms (e.g., patient portals, mobile apps, electronic health records) makes users more comfortable and confident. A consistent design reduces the learning curve and ensures ease of use, which is critical in high-stress healthcare environments.
Communication: Clear communication of information, such as notifications and lab results, is essential. A unified design system ensures that information is presented clearly, making it easier for patients and care providers to understand and act upon it.
Collaboration: A unified design system supports collaboration among diverse teams in care organizations by providing a common language and set of tools, reducing misunderstandings, and improving efficiency.
Accessibility: Accessibility is a legal and ethical requirement. Design systems ensure that applications are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by incorporating standards for color contrast, keyboard navigability, and screen reader compatibility.
Accelerating Innovation: Design systems enable care organizations to quickly develop and deploy new applications or features, responding rapidly to emerging health crises, regulatory changes, or new technological opportunities.
Reducing Costs: Streamlining the design and development process with a design system leads to cost savings. Reusable components and guidelines reduce the time and resources needed to create and maintain digital products.